Exercise
Set 12
EQUILIBRIUM GDP AND PRICES
I. Objectives
- To obtain equilibrium GDP
and price level in the DD/SS framework (also known as the AD-AS Model)
- To explain why output and
prices change
- To understand inflationary
and recessionary gaps
II. Data
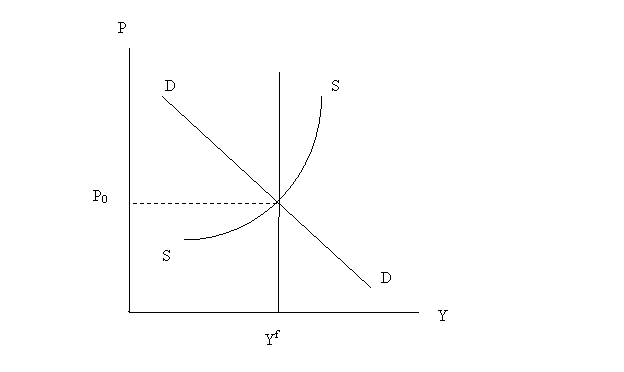
The figure below shows the
state of the economy. Aggregate demand is denoted by DD, aggregate
supply by SS, and Yf
represents potential output. P is the price level and Y is real GDP.
Note:
DD is also referred
to as AD (aggregate demand), SS is the same as SRAS (short-run
aggregate supply), and Yf
is the same as LRAS (long-run
aggregate supply).
III. Questions
- In the figure above, can we
conclude that the economy is
currently at
full employment? Explain.
- Suppose, in the figure
above, the government
increases spending on defense and roads.
- Describe the likely
effects on the economy. Provide a sketch.
- Will the economy
experience an inflationary gap or a recessionary gap? Explain.
- The gap in the previous
question will be eliminated through the self-correcting mechanism as
follows: Over time, wages will [
rise / fall ]
causing the SS curve to gradually shift [
left / right ]
until the economy reaches full employment. Provide a sketch and an
explanation.
- The Keynesian policy in the
previous question is an example of [
an expansionary / a contractionary ]
fiscal policy. Explain. Provide another example of a fiscal policy with
similar effects.
- In the 1970s, the US economy
experienced two severe oil crises.
- What were the reasons
for the crises? [Hint:
Events in the Middle East.]
- As a result of the oil
shocks, the price of oil rose dramatically. Explain how this led to
stagflation. Provide a sketch.
- In the last couple of
years, oil prices have risen sharply again. However, unlike during the
'70s, economic growth has remained robust with inflation remaining in
check. How come?
- The 1990s, especially the
second half of the decade, were characterized by large gains in
productivity, rapid economic growth and low inflation.
- Use the figure above to
explain the phenomenon.
- Discuss the reasons for
the robust gains in labor productivity.
- Generally, real
wages tend to rise with productivity. Why?
Video:
Solution to Section III
Questions at
http://www.screencast.com/t/uO0F7NhNt

