1. Measuring unemployment
- Based on BLS survey of 60,000 households every month
- Who is counted as employed?
- Who is counted as unemployed?
- Person doesn't have a job, and
- Has actively looked for jobs during previous week, or was temporarily laid off
- Discouraged workers are not in the labor force
- Unemployment rate:
- u = 100 x Unemployed/Labor force
2. Types of unemployment
- Frictional unemployment: Workers between jobs
- Structural unemployment: Due to changes in technology
- Cyclical unemployment: Linked to the business cycle
- Seasonal unemployment: Guess.
3. Full employment
- Does not mean zero unemployment (WHY?)
- Potential GDP (also full-employment output)
- The natural rate of unemployment (u*)
4. Unemployment insurance
- An automatic stabilizer:
Unemployment benefits tend to cushion the effects of a recession - Effect on job search?
5. Costs of high unemployment
- Loss in real GDP due to idle resources
- Actual GDP vs. Potential GDP (or full-employment output)
6. Comparison of labor markets in US and EU
- Flexible vs rigid labor markets:
The ease with which employers can fire workers - The generosity of the unemployment benefits scheme
Bureau of Labor Statistics
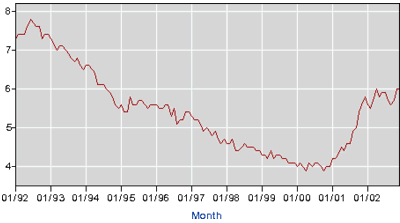
Unemployment
|