Exercise
Set 6.7
BUSINESS CYCLES
I. Objectives
- To understand what a
business cycle is
- To look at the history of
economic fluctuations
- To understand what
governments can do about business cycles
II. Defining a Business Cycle
is Not Easy
From
the NBER's website http://www.nber.org/cycles/recessions.html
(emphasis added):
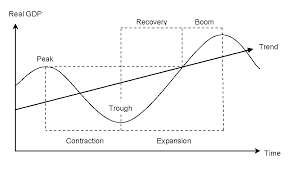
The NBER's Business Cycle Dating Committee maintains a chronology of
the U.S. business cycle. The chronology comprises alternating dates of
peaks and troughs in economic activity. A recession is a period
between a peak and a trough,
and an expansion is a period between a trough and a peak. During a recession, a
significant decline in economic activity spreads across the economy
and can last from a few months to more than a year.
 |
| http://www.mrmikeseconsite.co.cc/apmacro |
Similarly, during
an expansion, economic activity rises substantially,
spreads across the
economy, and usually lasts for several years.
In both recessions and
expansions, brief reversals in economic activity may occur-a recession
may include
a short period of expansion followed by further decline; an
expansion may include a short period of contraction followed by further
growth. The Committee applies its judgment based on the above
definitions of recessions and expansions and has no fixed rule to
determine whether a contraction is only a short interruption of an
expansion, or an expansion is only a short interruption of a
contraction. The most recent example of such a judgment that was less
than obvious was in 1980-1982, when the Committee determined that the
contraction that began
in 1981 was not a continuation of the one that
began in 1980, but rather a separate full recession.
The Committee does not have a fixed definition of economic activity. It
examines and compares the behavior of various
measures of broad
activity: real GDP
measured on the product and income sides, economy-wide employment,
and real
income. The Committee also
may consider indicators that do not cover the entire economy, such as
real sales and the Federal Reserve's
index of industrial
production
(IP). The Committee's use of these indicators in conjunction with the
broad measures recognizes the issue of double-counting of sectors
included in both those indicators and the broad measures. Still, a
well-defined peak or trough in real sales or IP might help to determine
the overall peak or trough dates, particularly if the economy-wide
indicators are in conflict or do not have well-defined peaks or
troughs. Use the Consumer Price Index
levels for two successive periods and compute the inflation rate.
III. Questions
- Go to the NBER website at http://www.nber.org/cycles.html
(opens in a new window).
- How long
did each of the following recessions last? (Use Duration for
Contraction: Peak to Trough)
- The
Great Depression
(1929-1933): __________ months
- The 1980s recession
(1981-1982): __________ months
- The "Great Recession"
(2007-09): __________ months
- Consider three
periods: The
pre-WWI period (1854-1919), the period between the World Wars
(1919-1945),
post-WWII period (1945-2009).
- In each period,
what
was
the average
duration of a contraction (in months)?
- Have recessions been
getting longer, or shorter, over time? What might be the reason for
this?
- Changes in taxes or
government spending constitute [ fiscal
/ monetary / trade
] policy, and are under the control of the [ President and Congress /
Federal Reserve / Supreme Court
].
- A change in money supply
(or
interest rates) constitutes [ fiscal
/ monetary / trade
] policy, and is under the control of the [ President and Congress /
Federal Reserve / Supreme Court
].
- Business cycles refer to
fluctuations in economic activity over the [ short run / long run ].
- Classical economists
generally regarded economies as self-regulating. This meant that, in
times of recession, they preferred the government to [ use fiscal policies / use
monetary policies / do nothing
].
- Keynesian economists
suggest
that, in times of recession, governments should
generally [ use fiscal
or monetary policies / do nothing
].
- According to a generally
accepted definition, a recession is said to occur when the
economy experiences _________ quarters, or _________ months, of falling
GDP. Note that this does not always coincide with NBER's definition:
see http://www.nber.org/cycles/recessions_faq.html.
Video:Solution
to Section III
Questions at
http://www.screencast.com/t/DP2t2Ijt