Lecture 10
THE INCOME-EXPENDITURE DIAGRAM
1. Aggregate expenditure vs. GDP
- Recall: AE = C + I + G + (X-IM)
- Case 1: AE < Y
With spending below ouput, inventories will start to climb.
Firms will then cut back on production, causing Y to decrease.
- Case 2: If AE > Y
Firms will produce more output (why?)
2. Equilibrium condition in the goods market
- Aggregate spending equals output
- Y = AE
- Y = C + I + G + (X-IM)
3. Model #1 (The base model)
- Objective: To determine the eqbm level of GDP in the economy
3.1 Assumptions
- Consumption (C)
- C increases with disposable income
- C = a + b(Y-T)
- Recall the parameters for the consumption function
- Investment (I)
- Assumed to be exogenous
- Level of investment is fixed
- Government spending (G)
- Assumed to be exogenous
- Level of govt. spending is fixed
- Net exports (X-IM)
- Assumed to be exogenous
- Level of net exports is fixed
- Taxes (T)
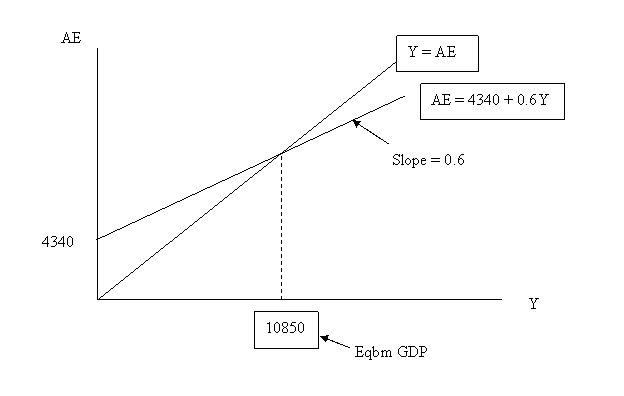
3.2 Income-Expenditure diagram
Step 1: Plot aggregate expenditure vs. GDP
Step 2: Plot 45-degree line through the origin
Step 3: Obtain the eqbm level of GDP
3.3 Analytical solution
Step 1: Obtain the expression for aggregate expenditure (AE) in
terms of Y
Step 2: Use the condition for eqbm in the goods market: Y = AE
Step 3: Solve for Y
3.4 Equilibrium consumption
- Graphically: Read off the value from the consumption function
- Analytically: Substitute the value of Y in the consumption function
3.5 Equilibrium saving
- Derive the saving function (in terms of GDP)
- Recall: S = DI - C
3.6 Example
Consider the following model of an economy:
C = 2000 + 0.6DI
T = 100
I = 800
G = 1200
X-IM = 400
Fig. Income–Expenditure Diagram
4. Relationship between S and I
- Recall: S = I + (G-T) + (X-IM)
4.1 Special cases
- Case 1: No government; No trade (closed economy)
G = 0, T = 0; X = 0, IM = 0
- Case 2: Closed economy
X = 0, IM = 0
5. Model #2
5.1 Assumptions
- Same as in Model #1, except that Imports are endogenous
- Import demand function: IM increases with GDP
- Marginal Propensity to Import (MPM): Coefficient of GDP
- Example: IM = 500 + 0.1Y
5.2 Income-expenditure diagram
- Slope of the AE-line is no longer equal to MPC
- Slope equals: MPC - MPM
5.3 Equilibrium
- Obtain eqbm values of: Y, C, S, Net Exports
[ EC101 home ]

