- By changing the interest paid on reserve balances (IORB) that banks hold in their accounts at a Federal Reserve Bank, the Fed can engineer an increase or decrease in the federal funds rate
Source: FRED blog
How does the Fed do it?
(NOTE: Since the Global Financial Crisis of 2007-09, the Fed has radically revamped the conduct of its monetary policy - see #5 below.)
Method 1: Open-market operations
Method 2: Changes in Interest on Reserve Balances (IORB)
Method 3: Changes in the discount rate

Source: FRED blog
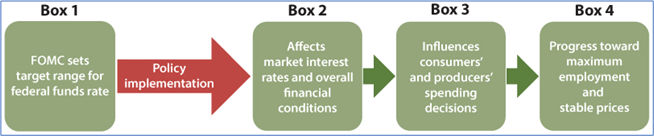
How does monetary policy work?Figure 1 provides an illustration of the transmission of monetary policy.
Source: Federal Reserve Board - Monetary Policy: What Are Its Goals? How Does It Work? |