Exercise Set 7.5
Duopoly
Two firms compete in a market. Demand is given by p = a - b(q + Q), where p is price, q is Firm A's output, and Q is Firm B's output. Firm A's marginal cost is c, Firm B's is C. Each firm has a fixed cost of f.
Suppose a = 800, b = 2, c = 440, C = 500, f = 10.
- Write Firm A's and Firm B's profit functions.
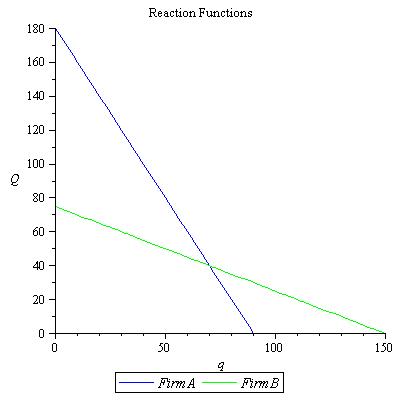
- Obtain Firm A's reaction function. Sketch it, with Q on the vertical axis. Indicate the intercepts and slope.
- Obtain Firm B's reaction function and sketch it. Indicate the intercepts and slope.
- Solve for the optimal values of q and Q. (This is the Nash equilibrium.)
- Obtain the price charged by both firms.
- Compute each firm's profits. Is B's profit smaller or larger than A's? Explain.
- If c increases, ceteris paribus, will Firm A produce more output or less? How about Firm B? Will the total output in the market increase or decrease? Will the price go up or down?
- Show the results of the increase in c on the reaction functions and the Nash equilibrium.
Answers: The initial Nash equilibrium occurs at q = 70, Q = 40. Firm B will make profits of 3190.
EC309 home

