Lecture 22
INCOME INEQUALITY
1. Efficiency and equity
Supply-side policies
- Eg., cut in capital gains tax
- Efficiency and equity effects
2. Income distribution and Wealth distribution
2.1 Poverty
- How the Census Bureau measures poverty: https://www.census.gov/topics/income-poverty/poverty/about.html
- The Federal poverty guideline
- Issued each year by the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS)
- Used to determine who receives federal subsidies or aid
- For a family of four in 2019: $25,926. [Source: Census poverty thresholds]
- Programs that use the poverty guideline to determine eligibility:
- Head Start
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) (formerly Food Stamp Program)
- Some parts of Medicaid
- Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP)
- Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
- In 2019, the official poverty rate was 10.5 percent. [Source: Income and Poverty in the U.S.]
- Number of people in poverty: 34 million.
- The 2019 U.S. median household income was $68,703.
- In 2019, 9.2% of people, or 29.6 million, were not covered by health insurance at the time of interview, according to the ACS, up from 8.9% and 28.6 million. [Source: Census/ACS]
2.2 Lorenz curve
- Measure of income inequality in a country
- Graph of Cumulative percentage of income vs Cumulative percentage of households
- Perfect equality is represented by the 45-degree line
- The greater the "sag" of the Lorenz curve, greater is the income inequality
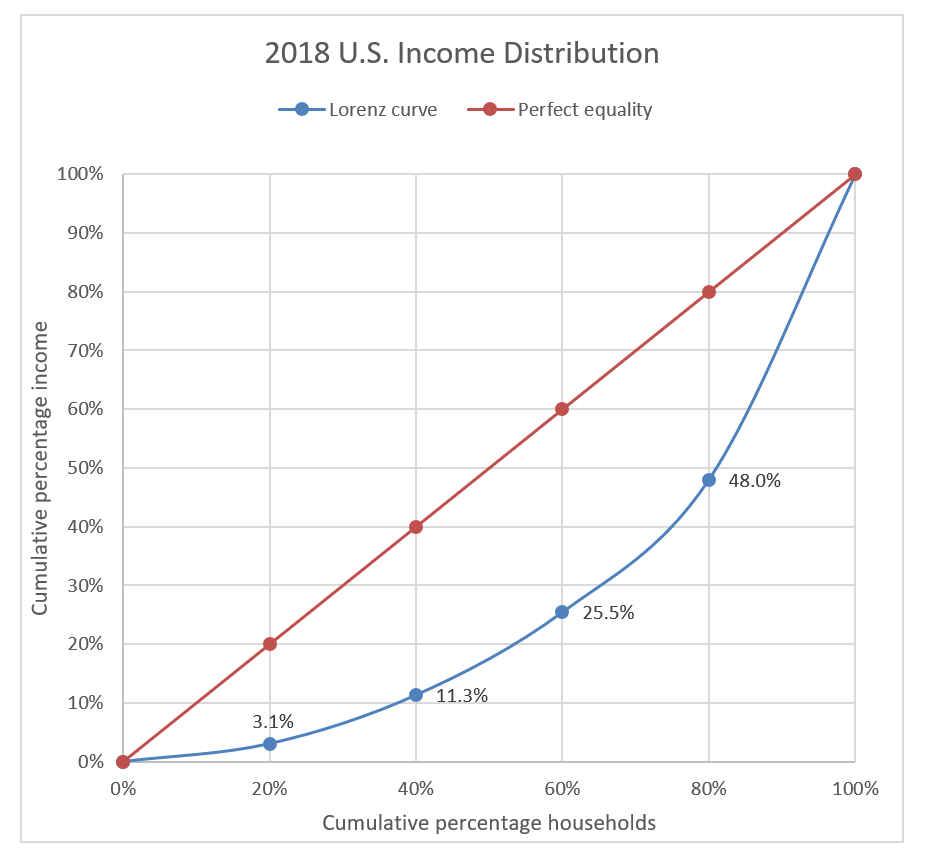
Source: Census Historical Tables H-1 and H-3
2.3 Gini coefficient
- Twice the area between the Lorenz curve and the 45-degree line
- Higher the coefficient, more is the inequality
- In 2019, Gini coefficent in the U.S. was 0.481. Source: census.gov
3. Reasons for income inequality
- Differences in:
- Ability
- Risk-taking
- Education
- Discrimination by employers, fellow workers
4. Income redistribution policies
(a) For those currently unemployed:
- Unemployment insurance
- Job-retraining programs
(b) For low-income workers:
- Minimum wage
- Earned-income tax credit (EITC)
(c) For low-income families:
(d) To ensure basic necessities for the poor:

