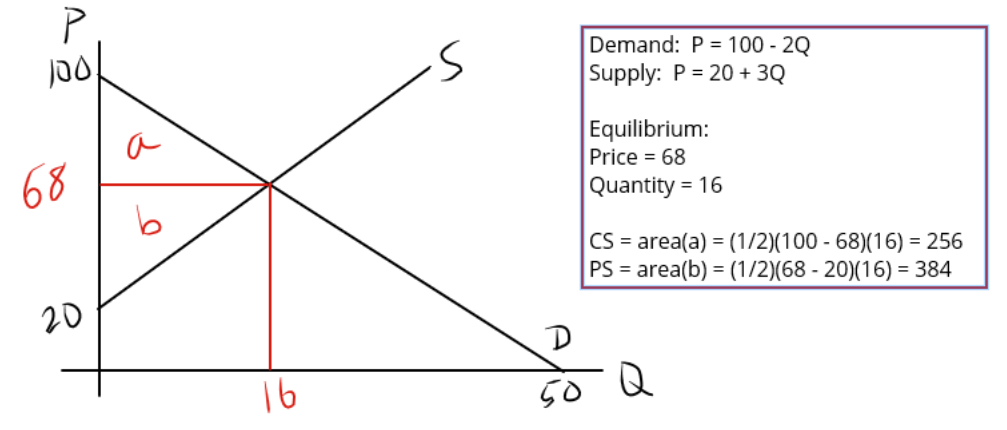
1. Consumer surplus (CS)
- Link between negative slope of DD curve and Law of diminishing marginal utility
- Difference between: The price the consumer is willing to pay for a unit of the good and the market price of the good
Measuring CS
- Area bounded by the demand curve above and market price below
- Area of a triangle (if demand is linear)
Effect of market price on CS
- Higher the price, lower the consumer surplus (why?)
2. Producer surplus (PS)
- The supply curve is the same as the firm's marginal cost curve
- Difference between price recd by the seller and the price at which seller is willing to sell a unit of the good
Measuring PS
- Area bounded by the market price above and supply curve below
- Area of a triangle (assuming linear supply)
Effect of market price on PS
- Higher the price, greater the producer surplus (why?)
3. Welfare
- Welfare is the sum of consumer surplus, producer surplus and govt. revenue (in the case of tariffs):
- W = CS + PS + R
- In the case of govt. subsidies, R is negative