Lecture 9
THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS ACCOUNTS
1. The BoP Accounts
It is the statistical record of all economic transactions taking place between a country's residents and the rest of the world.
- Current account [trade in goods and services]
- Capital account [trade in assets by the private sector]
- Official reserves account [foreign-exchange transactions by central banks]
2. Accounting rules
a. Sign (+ or -) of entry
Credit (+): If transaction results in receipts from foreigners
Debit (-): If transaction results in payment to foreigners
b. Double-entry bookkeeping
Every international transaction enters the balance of payments accounts twice (a credit and a debit).
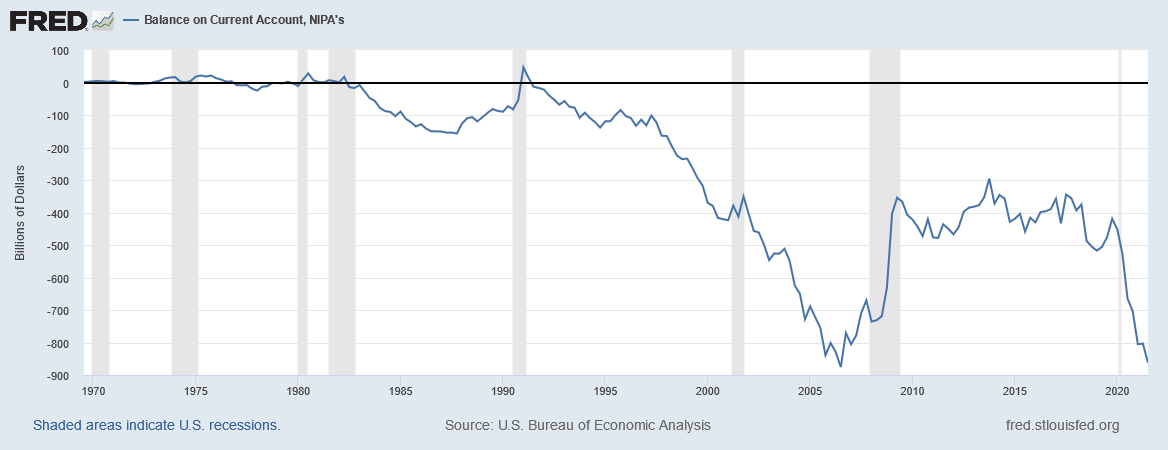
3. Current Account
(a) Merchandise trade:
- Exports and imports of goods
(b) Exports and imports of services:
- Tourism (expenditures by German tourists in Florida)
- Transportation (freight and insurance charges)
- Professional and other services (Management consulting fees, royalties, copyright fees)
(c) Investment income:
- Payments for the services of capital "working" abroad
- Interest payments and dividends
(d) Unilateral transfers:
- Government grants (foreign aid)
- Private remittances
- From emigrant workers to families
- Pensions to retired people living abroad
 4. Capital Account
4. Capital Account
(a) Foreign direct investment (FDI)
- A country's residents acquire control over a foreign firm:
- Buy enough stock (10%)
- Take over the firm outright
- Build a new factory
(b) Portfolio investment
- Short-term
- Maturity of 1 year or less
- Checking accounts in foreign banks
- Certificates of deposit in foreign banks
- Long-term
- Maturity greater than 1 year
- Stocks and bonds of foreign corporations
Credits (capital inflows)
- Increase in foreign ownership of U.S. assets
- Decrease in U.S. ownership of foreign assets
5. Official Reserve Transactions
Central bank transactions in international reserve assets:
- Gold
- Foreign exchange reserves ($, €, ¥)
- SDR's [Asset created by the IMF; value based on $, €, ¥, £, RMB]
Credits
- Increase in foreign reserve assets held in the U.S.
- Decline in the Fed's foreign-exchange reserves
Example 1: If ORT = $60 bn for Bank of China, it means that the Chinese central bank is selling $60 bn worth forex reserves.
Example 2: If ORT = -$20 bn for the Reserve Bank of India, it means that the Indian central bank is buying $20 bn worth forex reserves.
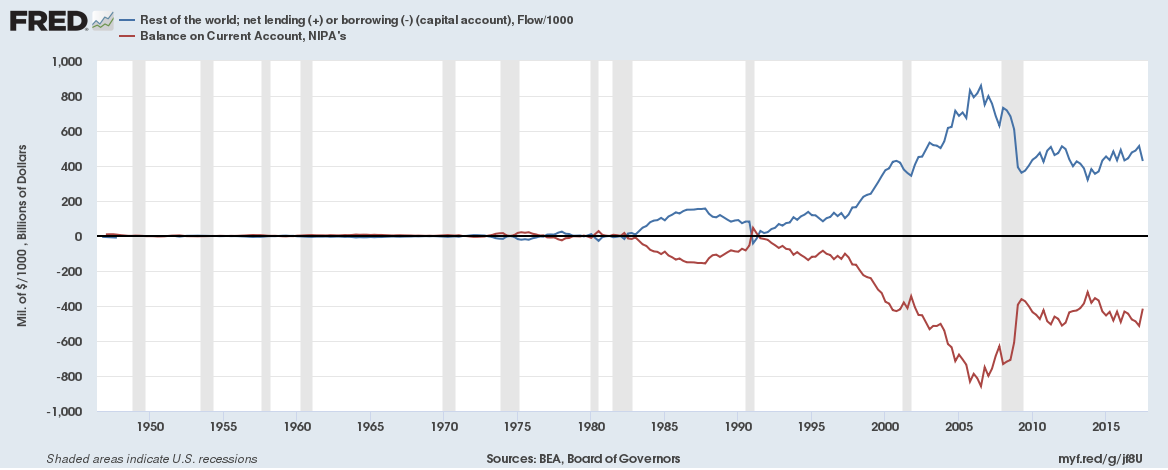
6. Official settlements balance or Balance of payments
- The sum of the current account and the capital account
- If the balance of payments is positive, the central bank is gaining foreign-exchange reserves
7. Statistical Discrepancy (SD)
- Measurement errors in trade data
- Incorrect valuation of transactions
- Fraud: Some transactions may not be reported
8. Notation
CA = current a/c balance
KA = capital a/c balance
ORT = official reserve transactions
SD = statistical discrepancy
BP = balance of payments (Official settlements balance)
9. Accounting Relationships
(1) CA + KA + ORT + SD = 0
(2) BP = CA + KA + SD
(3) ORT = -BP
Questions
- If the balance of payments is positive (a surplus) in a year, has there been an increase, or a decrease in the stock of official reserve assets? [Hint: Use eq (3).]
- Assume that the statistical discrepancy is zero. If a country's current account is in deficit, and private foreign investors do not buy any of the country's assets, is the central bank selling, or buying, foreign-exchange reserves?
Home

 4. Capital Account
4. Capital Account